Fx 0 Examples
We say "f of x equals x squared" what goes into the function is put inside parentheses after the name of the function:.
Fx 0 examples. The zero function is just the function such that \(0(x)=0\) for every \(x\). This isn't really a functions-operations question, but something like this often arises in the functions-operations context. Derivative examples Example #1.
This means the derivative will start out positive, approach 0, and then become negative:. In this example, the limit when x approaches 0 is equal to f(0) = 1. Hence an = 1 nπ R L L f 0 (x) sin nπx L dxand so j an 2L nπ max L x L f 0 (x) sin nπx L 2Lc nπ = k n:.
Divide f-2, the coefficient of the x term, by 2 to get \frac{f}{2}-1. However, we saw above that p x is uniformly continuous on (0;1). Label your graphs f or f ' appropriately.
A scalar multiple of a function is also differentiable, since the derivative commutes with scalar multiplication (\(\frac{d}{d x}(cf)=c\frac{d}{dx}f\)). This graph is positive when the slope of the tangent line here is positive. There exist left-hand limit \(\lim\limits_{x \to a – 0} f\left( x \right)\) and right-hand limit \(\lim\limits_{x \to a + 0} f\left( x \right)\);.
1.1 Approximation of functions Often it is desirable to approximate a function f by a simpler function g:. If F(x)=x has no real solution then also F(F(x)=x has no real solution. Example 8 f (x) = p x on I = (0;1).
Get more help from Chegg. Can be rewritten as. limx→0− 𝑓𝑥=limx→0+ 𝑓𝑥=𝑓(0) So, L.H.L = R.H.L.
The most common example of an indeterminate form occurs when determining the limit of the ratio of two functions, in which both of these functions tend to zero in the limit, and is referred to as "the indeterminate form /".For example, as approaches , the ratios /, /, and / go to ∞, , and respectively. Example of a non functional ordered pair with intergers between 0. Now f0 (x) = 1 2 p x, which is unbounded on I.
Then we’ll move on to part 2. Example 2 (d dx R x 0 e−t2. Find (f o f ) (x).
Let f(x) be a function measured in pounds, where x is mea- sured in feet. These one-sided limits are finite. O y=(sin x)/x 1 Figure 1 Loosely speaking, one might say that 1 is the ‘maximum value’ of f(x).
(-2)=5, f'(-2)=0 and f"(-2)=3. F' = (x + y z)' = (x + (y z))' AND (multiply) has a higher precedence than OR (add) = x' (y' + z') use dual or De Morgan’s Law = (x' + y y' + z z') (x x' + y' + z') expand 1st term by ORing it with y y' and z z', and 2nd term with x x'. Then add the square of \frac{f}{2}-1 to both sides of the equation.
X = –1, x = 3, and x = 1. This step makes the left hand side of the equation a perfect square. An approximate graph is indicated below.
Let Z = X/Y. What values of a and b, or what relation between a and b ensures the continuity/differentiability off and continuity of f'?. I know how to do it but I'd like to know how to read the answer straight off the graph $\endgroup$ – MyV Feb 17 '16 at 16:14.
So, for example, if this last graph is indeed the derivative of this first. Remarks • A continuous variable has infinite precision, hence P(X = x) = 0 for any x. F (x) = x 3 +5x 2 +x+8.
Find the values of and using the form. If f '(x) exists and is negative, then f(x) is decreasing at x 0. If f(x,y) is convex in (x,y) and C is a convex set, then g(x) = inf y∈C f(x,y) is convex examples • f(x,y) = xTAx+2xTBy +yTCy with A B BT C 0, C ≻ 0 minimizing over y gives g(x) = infy f(x,y) = xT(A−BC−1BT)x g is convex, hence Schur complement A−BC−1BT 0 • distance to a set:.
What are the units of F"(x)?. Inflection Points Definition of an inflection point:. We’ll first do some examples illustrating the use of part 1 of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
Hi John, I find it helps sometimes to think of a function as a machine, one where you give a number as input to the machine and receive a number as the output. This function comes in pieces;. • (x – a) is a factor of f(x).
Hence, the name "piecewise" function. When applying the chain rule:. It intersects the x-axis at the right place right over there.
Examples (i) Let X be the length of a randomly selected telephone call. Rewrite the function as an equation. Desmos offers best-in-class calculators, digital math activities, and curriculum to help every student love math and love learning math.
When I evaluate it at various x -values, I have to be careful to plug the argument into the correct piece of the function. Get 1:1 help now from expert Calculus tutors Solve it with our calculus problem solver and calculator. Then the second derivative at point x 0, f''(x 0), can indicate the type of that point:.
If h is positive, then the slope of the secant line from 0 to h is one, whereas if h is negative, then the slope of the secant line from 0 to h is negative one. We can see that f starts out with a positive slope (derivative), then has a slope (derivative) of zero, then has a negative slope (derivative):. Looking at the graph, it is clear that f(x) ≤ 1 for all x in the domain of f.
F (x) = lim f(x 0 + Δx) − f(x 0). But let's use "f":. F ' (x) = cos(3x 2) ⋅ 3x 2' = cos(3x 2) ⋅ 6x Second derivative test.
For example, the absolute value function given by f(x) = | x | is continuous at x = 0, but it is not differentiable there. What do the left and right behaviors (arrows of graph)of the function f(x)=-4n^3--5n^2+7n-4 look like?. The rest of the vector space properties are inherited from addition and scalar multiplication in \(\Re\).
Dist(x,S) = infy∈S kx−yk is convex if S is convex. In addition, we will define the gradient vector to help with some of the notation and work here. X → Function → y.
In the summation, this gives zero. F (x;y) 0 for all (x;y) f (x;y) = @ @x @ @y F(x;y) Z 1 1 Z 1 1 f (x;y) dx dy = 1 Statistics 104 (Colin Rundel) Lecture 17 March 26, 12 8 / 32 Section 5.1 Joint Distributions of Continuous RVs Marginal pdfs Marginal probability density functions are de ned in terms of \integrating out" one of the. With directional derivatives we can now ask how a function is changing if we allow all the independent variables to change rather than holding all but one constant as we had to do with partial derivatives.
Express F ' = (x + y z)' as a product of maxterms. Further there may be the following two options:. F '(x) = - 2 x + 6 f '(c) = - 2 c + 6 = 0 Solve the above equation to obtain c = 3 Therefore at x = 3 there is a tangent to the graph of f.
Domain of Composite Function. Hence, f is not Lipschitz continuous on I. Given the function f (x) as defined above, evaluate the function at the following values:.
Like, if we take z=x^2 - y^2, then z=(x+y)(x-y)=0 represents a pair of straight lines. If f '(x 0) does not exist or is zero, then the test tells fails. And at least over this interval, it seems it's positive from here to here.
Will provide no useful information. From the graph of f(x), draw a graph of f ' (x). The function \(f\left( x \right)\) has a discontinuity of the first kind at \(x = a\) if.
F ' (x) = 3x 2 +2⋅5x+1+0 = 3x 2 +10x+1 Example #2. By above an = 1 nπ R L L f 0 (x) sin nπx L dx = L n2π2 f 0 (x. Our math solver supports basic math, pre-algebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.
Because of orthogonality, we can compute the b n very simply:. Solve your math problems using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions. It is a different way of writing "y" in equations, but it's much more useful!.
Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) Example (Monitoring a chemical process) The output of a chemical process is continually monitored to ensure. Give an example of a function wheref'(x) = 0 and F"(x) = 0. The first derivative test:.
{ x | x ≥ 0} Or using interval notation it is:. Here is F(x) for the widget example:. F(x) = x 2 shows us that function "f" takes "x" and squares it.
X and Y are jointly continuous with joint pdf f(x,y) = (e−(x+y) if 0 ≤ x, 0 ≤ y 0, otherwise. Find the pdf of Z. • The zero of the function f(x) is a.
(ii) Since f 00is a bounded function on R, there exists a constant c1 such that j f x c1 for all x 2 R. F(x) = 8 >> >> < >> >>:. (The graph of y = x 1 is a hyperbola in the.
• f(a) = 0. Determine whether x + 1 is a factor of the following polynomials. F (x) = sin(3x 2).
In each case, if the limits of the numerator and denominator are substituted, the. Tap for more steps. When the first derivative of a function is zero at point x 0.
The first thing we do is draw a picture of the support set (which in this case is the first. $\begingroup$ For which values of x will will f (x).f'(x) < 0 $\endgroup$ – MyV Feb 17 '16 at 16:12 $\begingroup$ No. Given f (x) = 3x 2 – x + 4, find the simplified form of the following expression, and evaluate at h = 0:.
Fourier Sine Series Examples 16th November 07 The Fourier sine series for a function f(x) defined on x ∈ 0,1 writes f(x) as f(x) = X∞ n=1 b n sin(nπx) for some coefficients b n. A function may be thought of as a rule which takes each member x of a set and assigns, or maps it to the same value y known at its image. F(x) = √x and g(x) = x 2.
Example 3Discuss the continuity of the function f given by 𝑓(𝑥) = | 𝑥 | 𝑎𝑡 𝑥 = 0. 𝑓(𝑥) = |𝑥| 𝑓𝑥= −𝑥, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥<0𝑥, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥 ≥0f is continuous at 𝑥 = 0 if L.H.L = R.H.L = 𝑓(0) i.e. (ii) Let X be the volume of coke in a can marketed as 12oz.
Use the slope-intercept form to find the slope and y-intercept. As an extension of Examples 1.1.6 and 1.1.7, investigate a function given by 24 sin if 270, f(x) = 0, if x = 0, a, b, € R. Suppose also that the function \(f\left( x \right)\) is a single valued, piecewise continuous (must have a finite number of jump discontinuities), and piecewise monotonic (must have a finite number of maxima and minima).
F(x) R 1 1 f (x)dx = 1 Bivariate de nition:. Each f(x) for x>1 is x plus the sum of the numbers from 1 to (x-1) + 1 Remember, f(0)=1 So, for example, the f(4)=11 because it is 4 + sum of the numbers from 1 to 3 + 1. Math · AP®︎.
When I think of y=f(x), i Think of y = f(x)= 1, x = 1, x =2, then y =f(x) =2, x =3, then y= f(x)=3, and so on. The slope-intercept form is , where is the slope and is the y-intercept. F '(x 0) = 0.
Can be rewritten as can be rewritten as need not be rewritten. So f(x) shows us the function is called "f", and "x" goes in. Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor.
In the relation , there are many values of that can be paired with more than one value of - for example,. EXAMPLE 3 2 1 y x 3 1 y x (0, 2) ( 2, 0) (0, 0) (2, 2) Page 1 of 2 116 Chapter 2 Linear Equations and Functions USING PIECEWISE FUNCTIONS IN REAL LIFE Using a Step Function a.Write and graph a piecewise function for the parking charges shown on the sign. F(1) = f(5) = - 1 and f is continuous on 1 , 5 and differentiable on (1 , 5) hence, according to Rolle's theorem, there exists at least one value of x = c such that f '(c) = 0.
A letter such as f, g or h is often used to stand for a function.The Function which squares a number and adds on a 3, can be written as f(x) = x 2 + 5.The same notion may also be used to show how a function affects particular values. If we say, f(x,y)=0 then it represents only one point on the parabola:Origin. In the section we introduce the concept of directional derivatives.
• In this case, the p.m.f. 0), f x sin nπx L j L L 0. A) Let f(x) = 3x 4 + x 3 – x 2 + 3x + 2.
= Σ(0, 1, 2) sum of 0-minterms Example. B.What are the domain and range of the function?. To do this we will use the formula:.
0 if x < 0 0:550 if 0 x < 1 0:800 if 1 x < 2 0:975 if 2 x < 3 1:0000 if x 3 19/23. This graph shows that as x approaches - 2 from the left, f(x) gets smaller and smaller without bound and there is no limit. Example.In this example, we find the second order Taylor expansion of f(x,y) = p 1+ 4x2 +y2 about (x0,y0) = (1,2) and use it to compute approximately f(1.1,2.05).We first compute all partial derivatives up to order 2 at (x0,y0).
For any given m, we integrate both sides against sin(mπx). • The remainder is zero when f(x) is divided by (x – a). The point (-2,5) is which of the following for the graph of f?.
We must get both Domains right (the composed function and the first function used). If f '(x 0) exists and is positive, then f '(x) is increasing at x 0. Δx→0 Δx Graphically, we will be finding the slope of the tangent line at at an arbitrary point (x 0, 1 x 1 0) on the graph of y = x.
Furthermore, 1 is the smallest number which is greater than all of f’s values. So, if f(x) = 0, it does not necessarily mean F(x) = 0. • The solution to f(x) = 0 is a.
A similar argument shows that j bn k n. Example 1 The graph of f(x) = - x 2 + 6x - 6 for 1 ≤ x ≤ 5 is shown below. A) 3x 4 + x 3 – x 2 + 3x + 2 b) x 6 + 2x(x – 1) – 4.
To demonstrate that is a function of in the other examples, we solve each for :. F(x) = x We’ll find the derivative of the function f(x) = x1. And we usually see what a function does with the input:.
0,+∞) It is important to get the Domain right, or we will get bad results!. Free functions calculator - explore function domain, range, intercepts, extreme points and asymptotes step-by-step.

Notes On Topics Of Algebra Notes
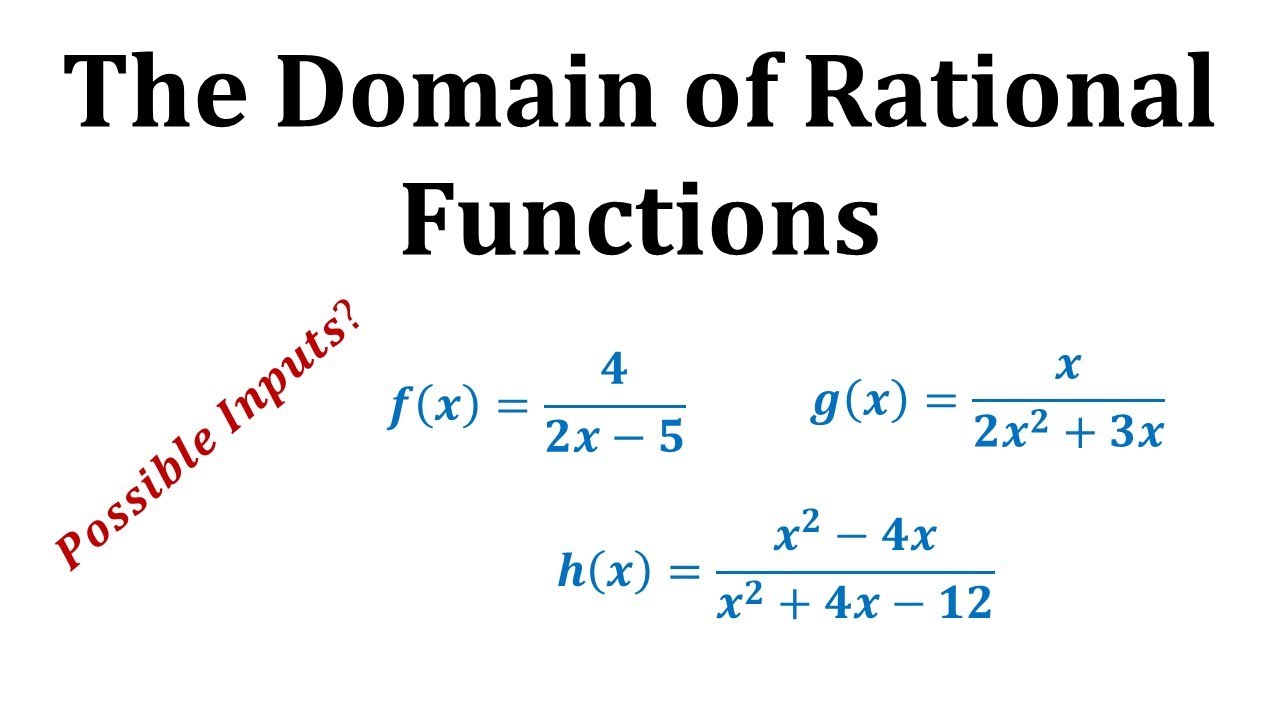
Find The Domain Of A Function Defined By An Equation College Algebra

Domain And Range Of Quadratic Functions Video Khan Academy
Fx 0 Examples のギャラリー

Derivative And Tangent Line

Limits And Continuity Pdf Free Download
Mhf4u1 8 4p2 Examples
3
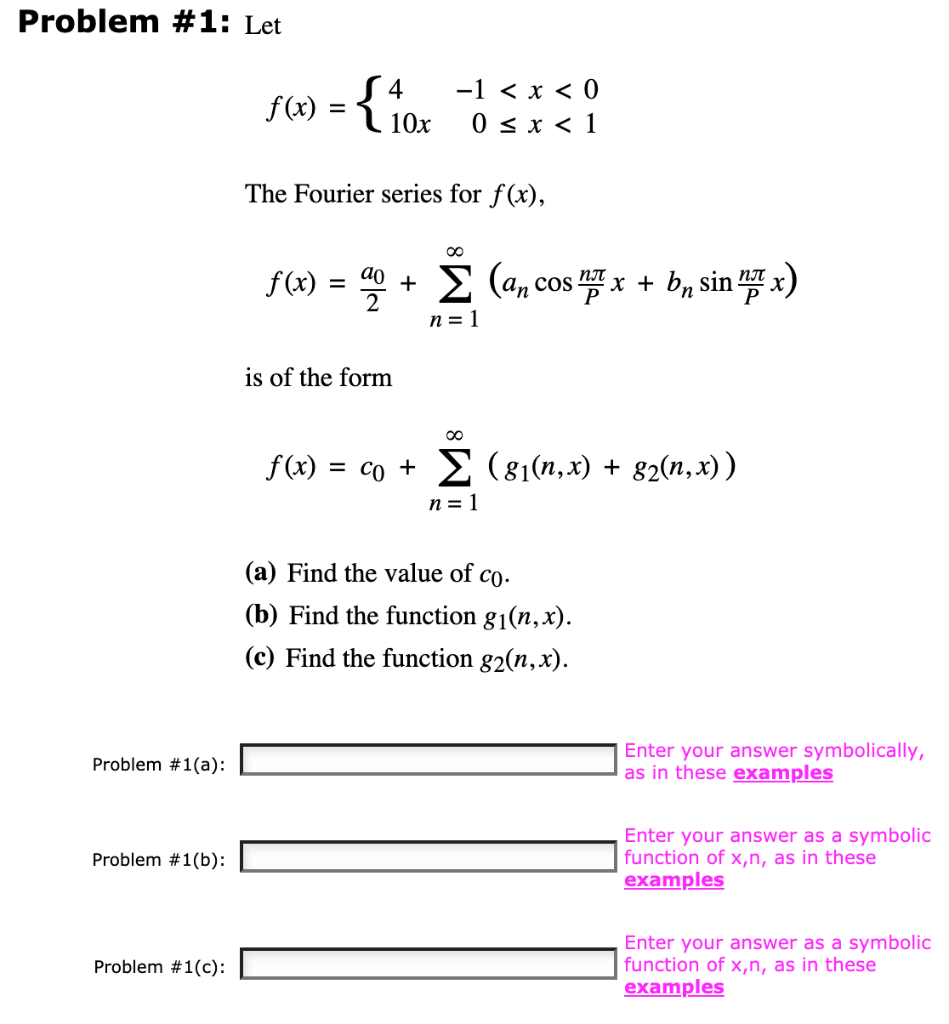
Solved Problem 1 Let S4 F X 1 X 0 0 X 1 1 Chegg Com

Function Mathematics Wikipedia

Solved 8 Find Examples Of Functions F And G Defined On Chegg Com
Sage Calculus Tutorial Continuity

Example 8 Find Derivative Of F X 3 At X 0 X 3 Examples
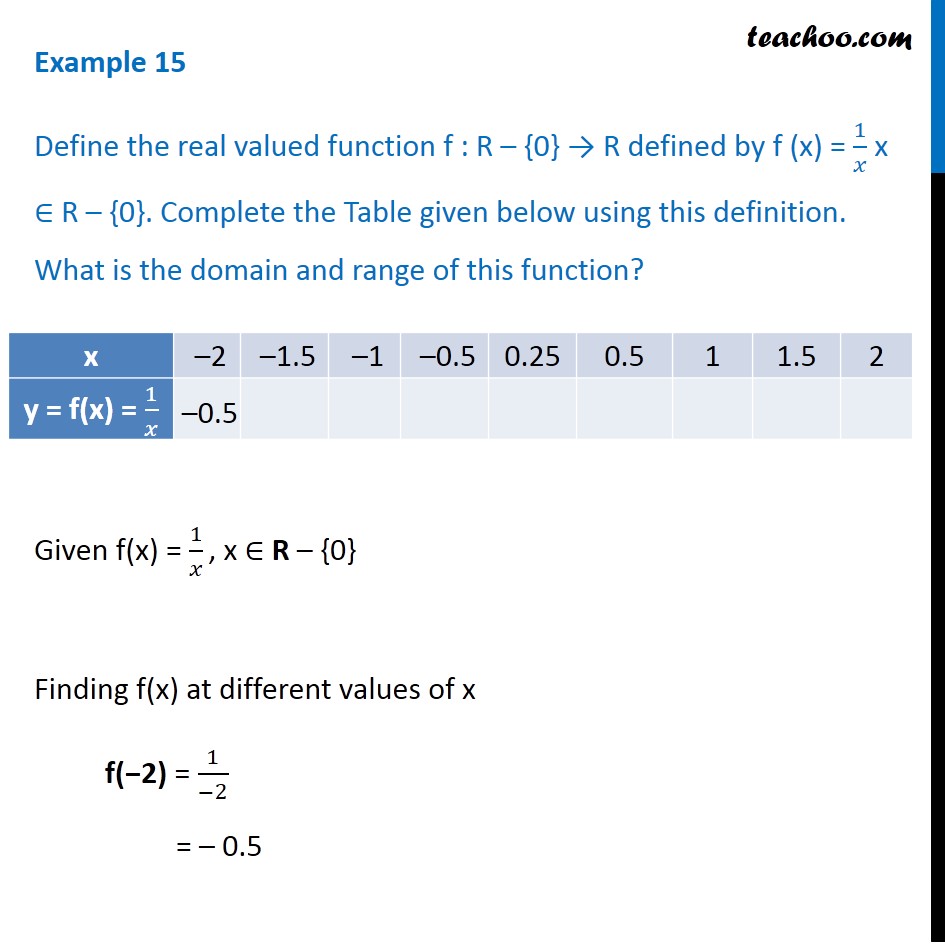
Example 15 F X 1 X What Is The Domain And Range Examples

What Is A Function

One Sided Limits Read Calculus Ck 12 Foundation

2280 Week 4 Lectures S17

Fexamples Html
Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0
Features Of Function Graphs Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math
Examples Friday Feb 21

Example 9 Discuss Continuity Of F X 1 X Chapter 5
Sage Calculus Tutorial Continuity
2
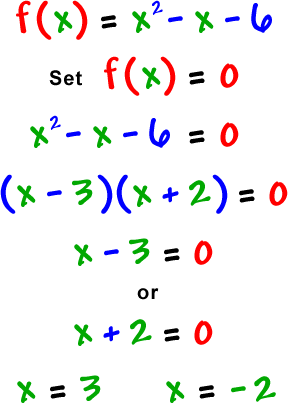
Real Zeros 1
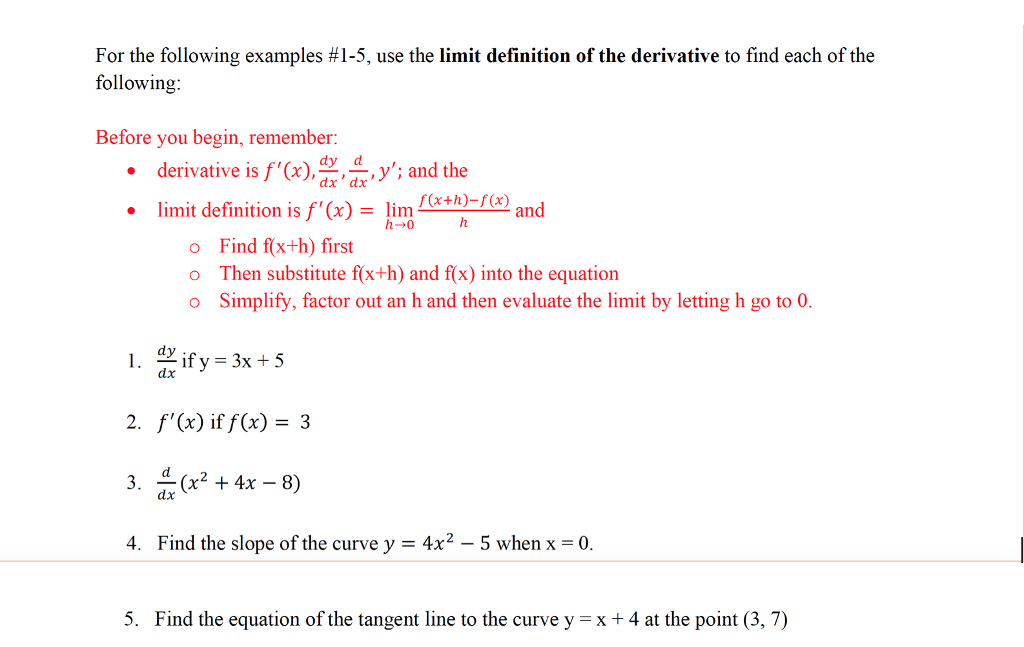
Solved For The Following Examples 1 5 Use The Limit Def Chegg Com

Chapter 2 Maths 3

Continuity At A Point Video Khan Academy

Example 13 Find Intervals Where F X Sin X Cos X Is
2

Answered 1 What Does The Continuity Of A Bartleby

Function Definition Types Examples Facts Britannica
Examples Of Separable Classes The First Example Is Linearly Separable Download Scientific Diagram
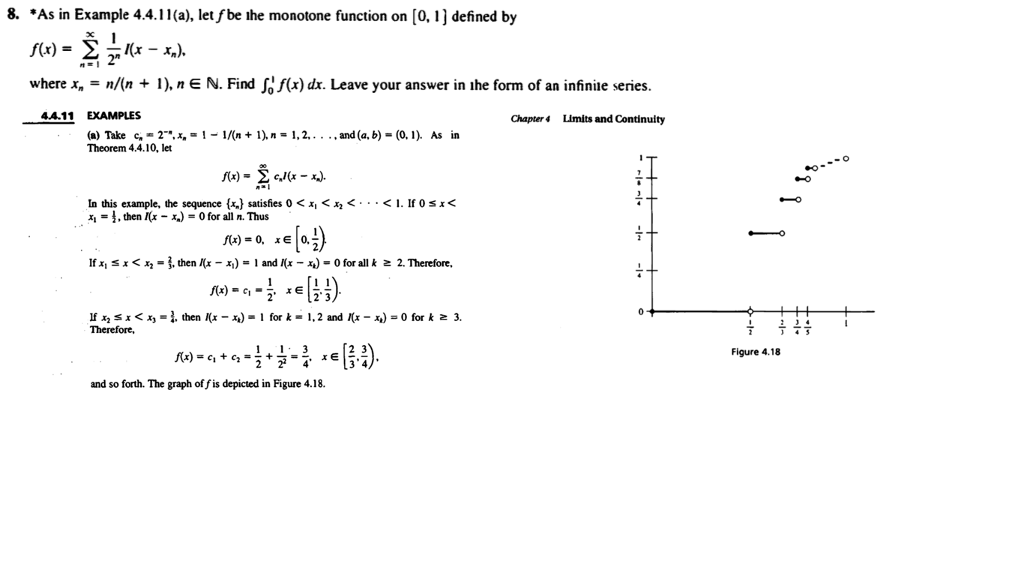
Let F Be The Monotone Function On 0 1 Defined B Chegg Com

Notes Math 414 Narcowich Spring 04

L Hopital S Rule Wikipedia
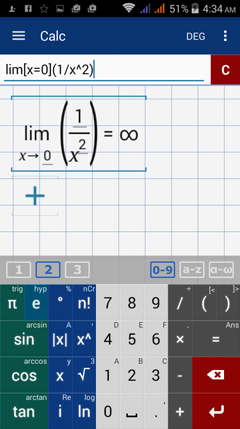
15 5 Limit Of A Rational Function Graphing Calculator By Mathlab User Manual

Misc 6 Give Examples Of F G Such That Gof Is Injective
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrldxsx0qdakuduyffqgu8o7dafgbv3gmdvlxublmdnzgypuqkn Usqp Cau
2
What Does F 0 Represent On The Graph Of F X Quora
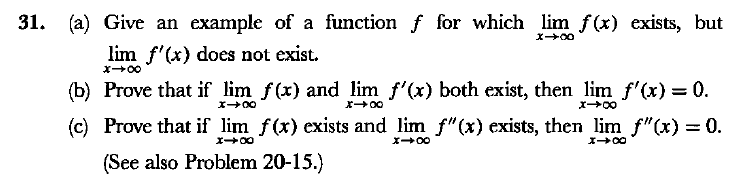
Solved 31 A Give An Example Of A Function F For Which Chegg Com
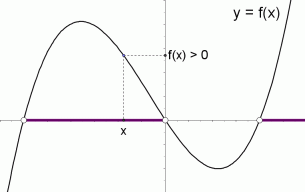
Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0
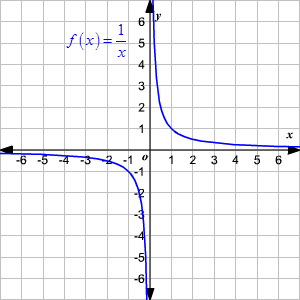
Domain And Range Of Rational Functions

5 2 Solved Examples Short Answer S A Example 1 Find The Value Of The Constant K
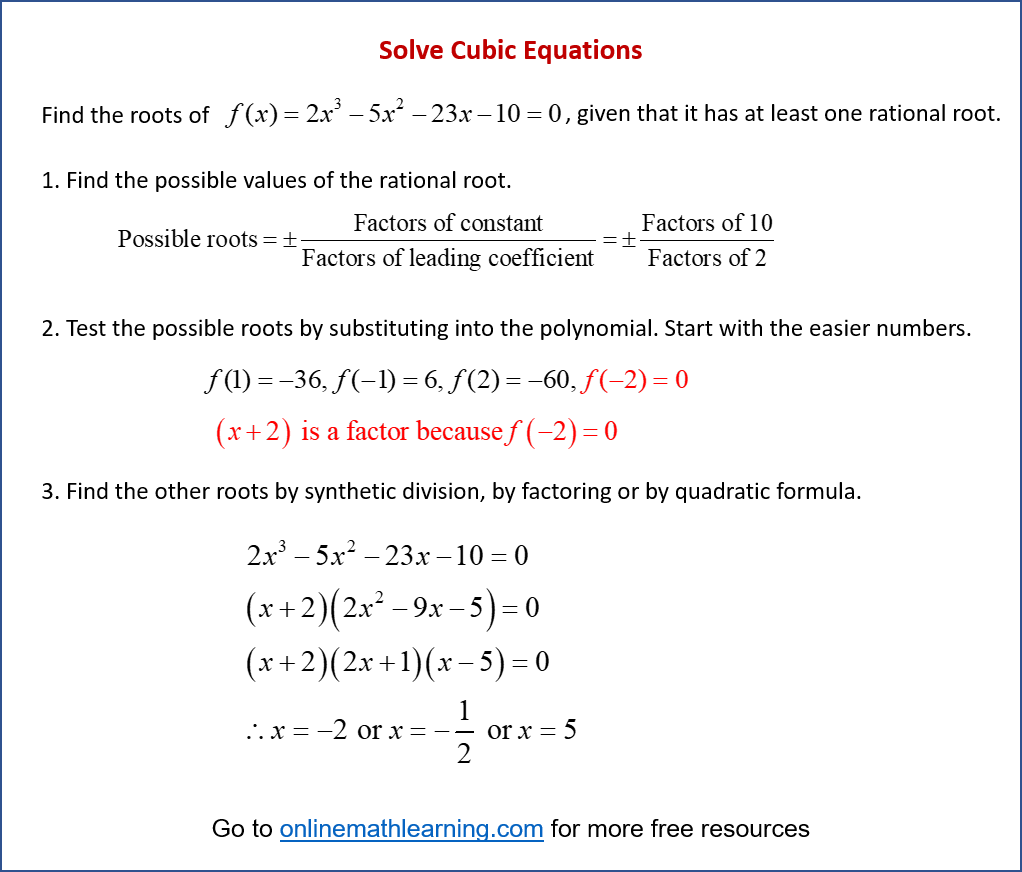
Solving Cubic Equations Solutions Examples Videos
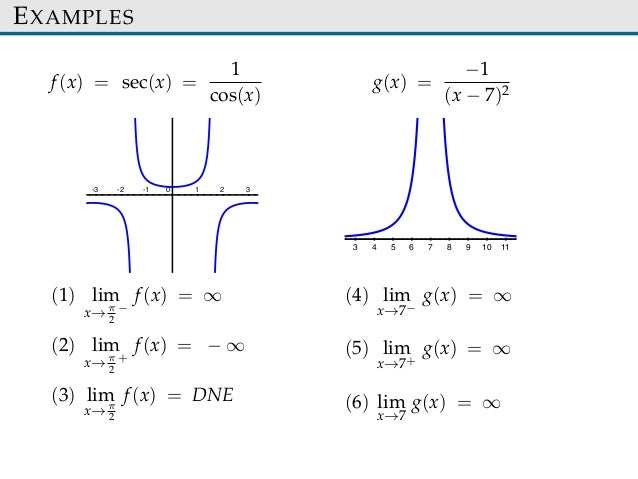
Limite Functions Sect22 24

Compute F A Algebraically For The Given Value Of A Hint See Example 1 F X Homeworklib

Give An Example Of Polynomials F X G X Q X And R X

Solved 3 Define A Periodic Function F X As Follows X Chegg Com

The Study Economics For Ma Ignou Microeconomics Macroeconomics Econometrics Mathmatical Economics Graphical Representation Of Functions

Even And Odd Functions Equations Video Khan Academy
Pathological Taylor Series Stuff

2 Xf ˇ X Yf ˇ X F ˇ X And Lim W X 0 S F X ˇ X For Download Scientific Diagram

2 3 Differentiable Functions Of One Variable Definition Of Pages 1 12 Text Version Anyflip

Answered 2 Graphs And Functions Graph Each Bartleby

Solved Give An Example Of Functions F And G Both Continu Chegg Com
Inverse Of Quadratic Function Chilimath
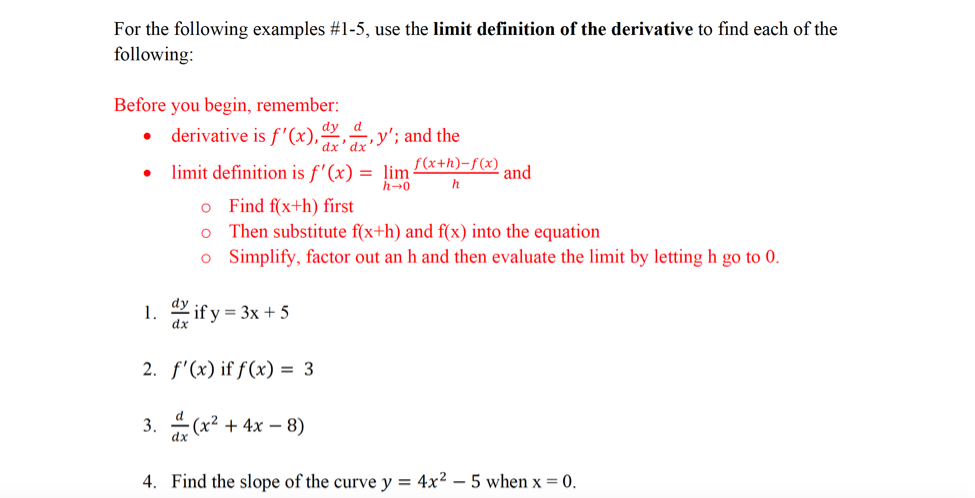
Solved For The Following Examples 1 5 Use The Limit Def Chegg Com

Example 11 Find Derivative Of Constant Function F X A

Continuity Differentiability Arbindsingh Com Pages 1 50 Text Version Anyflip
2
2

Differentiable

Solved Problem 1 Let F X 57 4x 1 X 0 0 X Chegg Com

Solved Let C Be A Constant Then If F X C Its Derivati Chegg Com
2
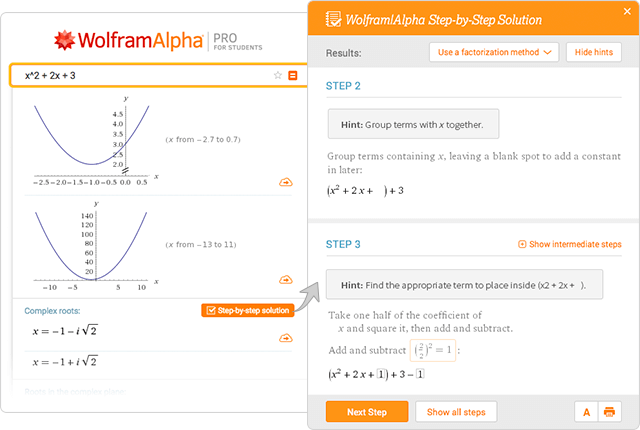
Wolfram Alpha Examples Step By Step Solutions
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqucyhwhlsxc2ds Zseqrowq2i8i2w9k56mzeh4etffh9zkkijf Usqp Cau

Example 2 Examine Whether F X X2 Is Continuous At X 0

The Graph Of F Is Given Use The Graph To Compute The Quantities Asked For If A 4 A Lim X To 0 F X B Lim X To 4 F X C Lim X To 0 F X D Lim X To 4 F X
2
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqf 2wo9hzoefkoeih4hsp60v Yapppvbeducgjrmn2ij34j4hx Usqp Cau
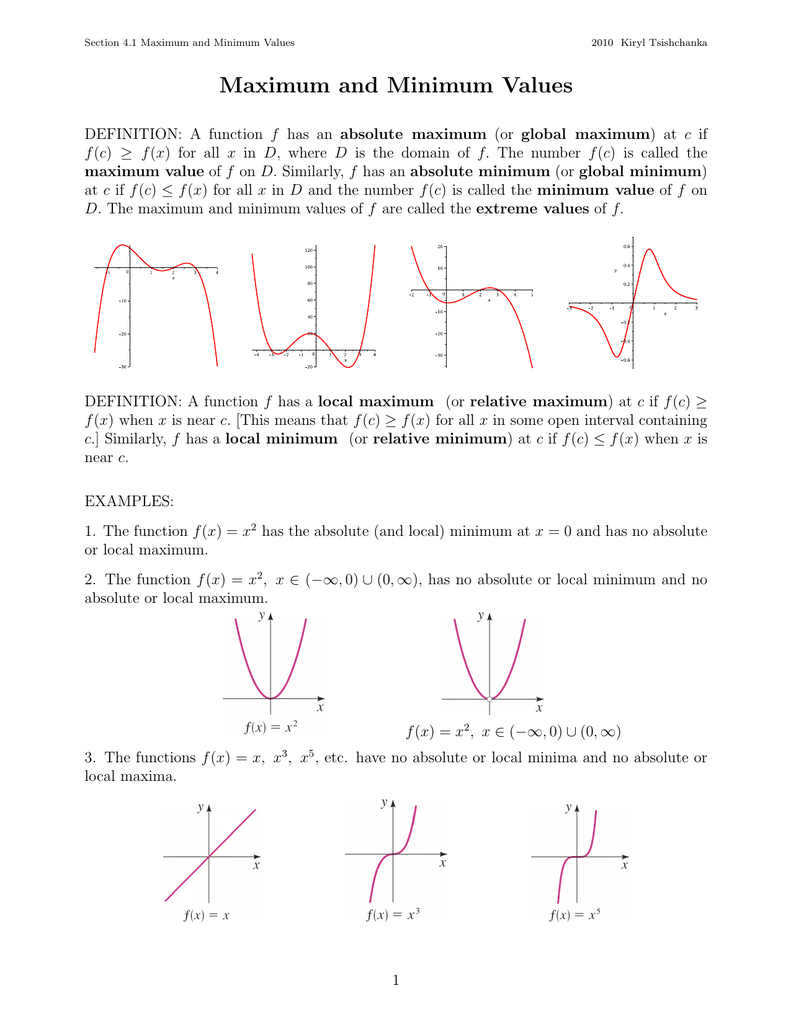
Maximum And Minimum Values

Example 13 Discuss Continuity Of F X X X 0 And X 2 X 0
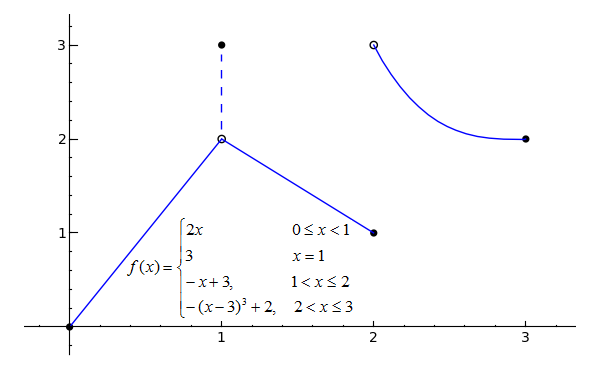
Sage Calculus Tutorial Continuity

Piecewise Defined Functions College Algebra

How To Find Zeros Of A Function
2
2
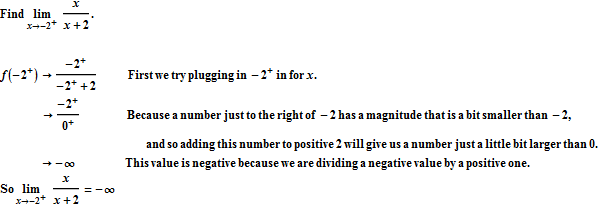
Finding Limits Algebraically
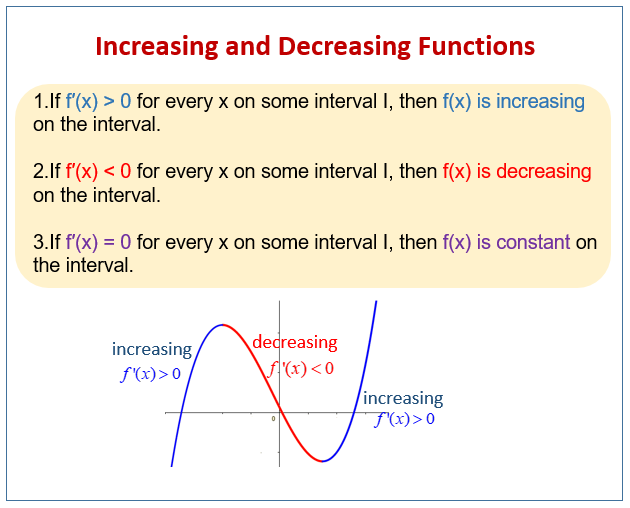
Increasing And Decreasing Functions Examples Solutions Worksheets Videos Activities

Lesson 65

52 Differentiation 8 Find Examples Of Functions Chegg Com

Derivative And Tangent Line

Example 13 Find Intervals Where F X Sin X Cos X Is
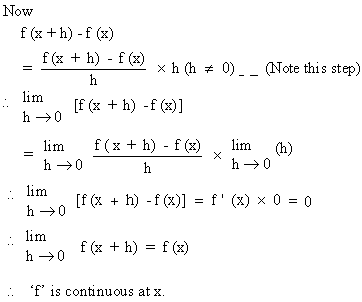
Pinkmonkey Com Calculus Study Guide Section 4 3 Derivability And Continuity Of A Function At A Point

Graphs Of F X F X F X And X 0 F T Dt For Example 29 5 Download Scientific Diagram
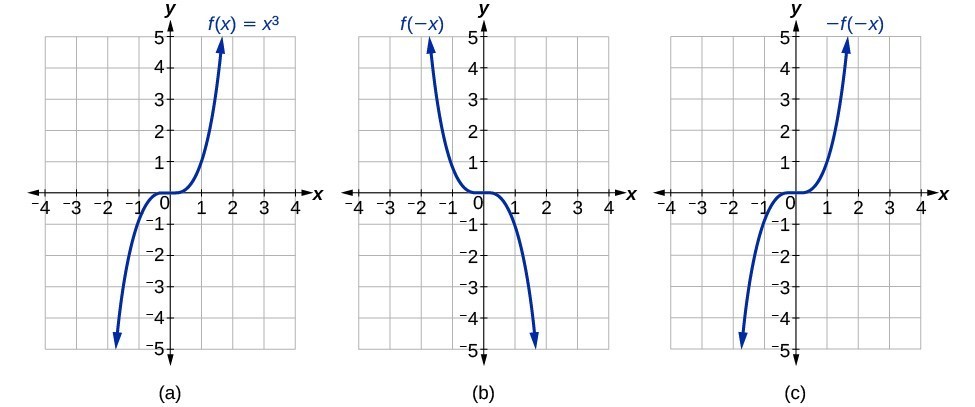
Determine Whether A Function Is Even Odd Or Neither From Its Graph Math 1314 College Algebra

I The Sum Difference Product And Quotient Functions Pages 1 3 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
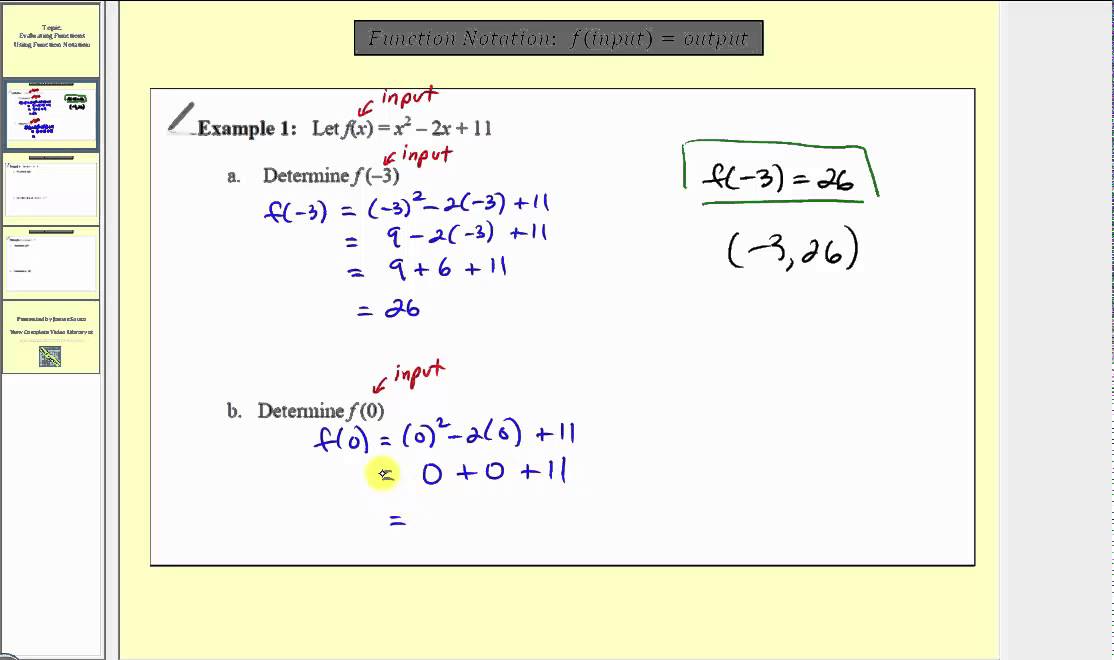
Evaluating And Solving Functions College Algebra

Example 3 Discuss Continuity Of F X X At X 0 Class 12
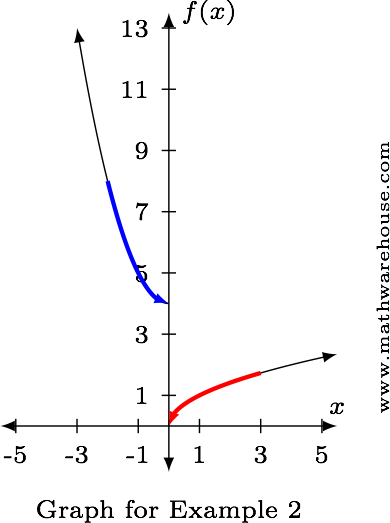
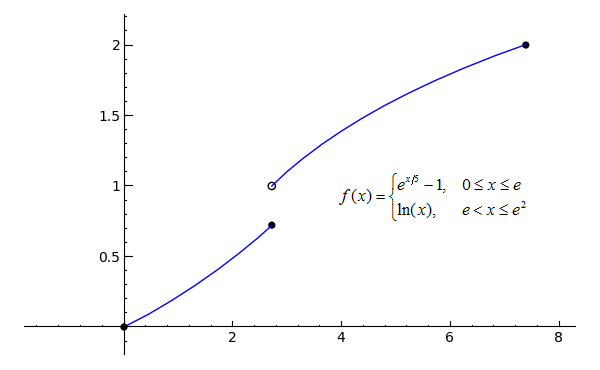
Limits Of Piecewise Defined Functions How To Calculate Examples Practice Problems Pictures
Untitled Document

Answered A Suppose You Have Two Functions F X Bartleby

Defining Domains Making Inverse Functions Combining Functions Underground Mathematics

Solved For Each Of The Following Functions Find A F 4 Chegg Com
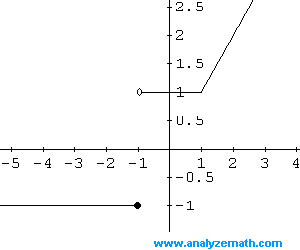
Graph Piecewise Functions
2

Factor Theorem Solutions Examples Videos

Regula Falsi Method For Finding Root Of A Polynomial
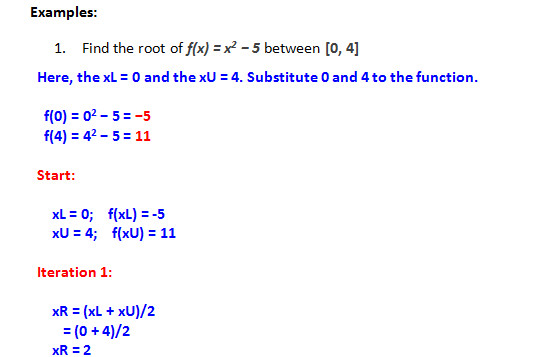
Bisection Method Numerical Methods
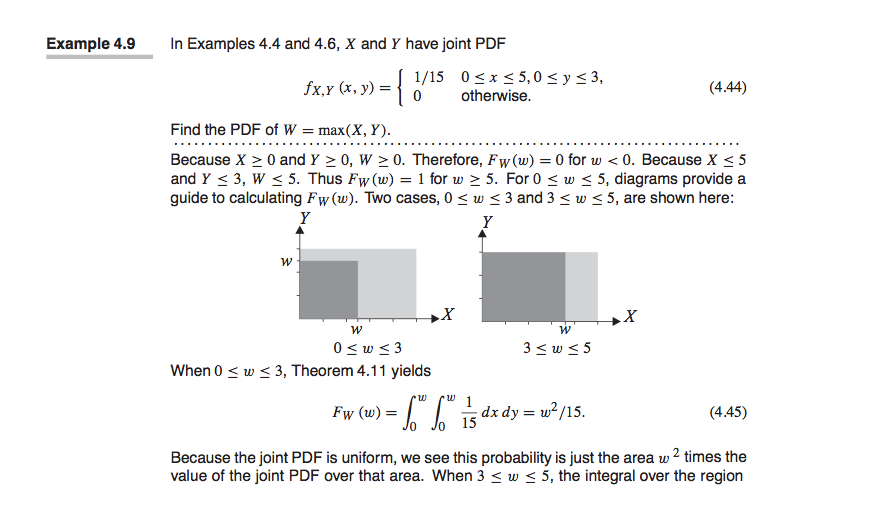
Solved Consider Example 4 9 A This Time We Modify The D Chegg Com

Find X Such That F X 0 Example 1 Youtube

Limit Calculator Wolfram Alpha



